The
Language of film analysis
|
CAMERA RANGE (=the distance between the camera and object) |
|||
|
extreme long shot (super totale Einstellung) |
shot of, e.g. a large crowd scene or a view of
scenery as far as the horizon "What
is the effect of the ~?" |
|
|
|
long shot |
a view of a situation or setting from a distance "the
camera pulls away from the close-ups to a long shot of the Boston skyline." |
|
|
|
medium
long shot (halb totale Einstellung) |
|
|
|
|
full
shot (Halbnaheinstellung) |
|
|
|
|
medium shot, mid shot, medium close shot ("amerikanische
Einstellung") |
shows a subject down to his or her waist, e.g.
showing head and shoulders of two people in conversation "What
is the purpose of the high angle medium close shot?" |
|
|
|
close-up (Großaufnahme) |
a full-screen shot o f a subject's face, showing
the finest nuances of expression "The
camera suddenly cuts to a close-up." "What
does the series of close-ups show?" |
|
|
|
extreme close-up (shot) detail
(shot) (Detailaufnahme) |
a shot of a hand, eye, mouth or object in detail |
|
|
|
POINT OF VIEW (VIEWPOINTS) (= the position from which the camera is
filming) |
|||
|
establishing shot |
often used at the beginning of a scene to
indicate the location or setting, it is usually a long shot taken from a
neutral position "The
scene starts with an ~." |
||
|
point-of-view shot, POV-shot (subjektive Einstellung) |
shows a scene from the perspective of a character |
||
|
over-the-shoulder shot |
often used in dialogue scenes, a frontal view o f
a dialogue partner from the perspective of someone standing behind and
slightly to the side of the other partner, so that parts of both can be seen |
||
|
reaction
shot (Gegeneinstellung) |
short shot of a character's response to an action "He
decided to hold a ~." |
||
|
insert (shot) |
a detail shot which
quickly gives visual information necessary to understand the meaning of a
scene, for example a newspaper page, or a physical detail |
||
|
reverse-angle shot |
a shot from the opposite perspective, e.g. after
an over-the-shoulder shot |
||
|
hand-held camera |
"What
effect does the ~ have in the party scene?" |
||
|
CAMERA
ANGLES (= Kameraperspektive) |
|||
|
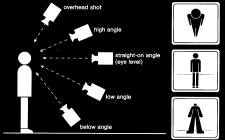
aerial shot or high
angle or overhead (Vogelperspektive) |
long or extreme long shot of the ground from the
air "How
does the sequence of aerial and tracking shots support the voiceover
commentary?" |
|
|
|
high-angle shot |
shows people or objects from \ above, i.e. higher
than eye level |
||
|
low-angle shot or below
shot (Froschperspektive) |
shows people or objects from below, i.e. lower
than eye level |
||
|
eye-level shot or straight-on angle |
views a subject from the level of a person's eyes "In
the first part the straight-on angle of the camera puts the viewer on the
same level as Mrs Robinson." |
||
|
"How
do the varoius camera shot angles highlight the power of Mrs Robinson?" |
|
|
|
CAMERA MOVEMENT (movement of the camera during a shot) |
|||
|
pan(ning shot) (horizontaler Schwenk) |
the camera pans (moves horizontally) from left to
right or vice versa across the picture "The
camera pans across the picture." |
||
|
tilt
(shot) (vertikaler Schwenk) |
the camera tilts up (moves upwards) or tilts
down (moves downwards) around a vertical line |
||
|
tracking shot / trucking shot |
|
||
|
zoom |
the stationary camera appears to approach a
subject by 'zooming in' ; or to move farther away by 'zooming out' "The
camera zooms in(zooms out) on Ben's face." |
||
|
EDITING / Montage (= the arrangement of shots in a structured
sequence) |
|||
|
master shot |
main shot of a whole scene taken by one camera in
one position, which is then intercut with other shots to add interest |
||
|
cutaway |
shot of something not shown by the master shot of
a scene, but connected to the main action in some way |
||
|
cross-cutting or parallel action |
intermingling the shots of two or more scenes
which are taking place at the same time |
||
|
flashback (Rückblende) |
a scene or sequence dealing with the past which
is inserted into a film's 'present time' |
||
|
flash-forward (Vorausschau) |
a scene or sequence which looks into the future |
||
|
match cut |
two scenes connected by visual or aural
parallelism, e.g. one door closing and then another one opening |
||
|
split
screen (Bildteilung) |
division of the screen to show two or more
pictures at the same time |
||
|
PUNCTUATION (= the way in which shots are linked) |
|||
|
casting (Besetzung) |
choosing actors to impersonate the characters |
||
|
cut |
a switch from one image or shot to another "What
effect does the sudden cut from the pool to Ben's room have on the viewer?" |
||
|
jump-cut |
(a) switching back and forth between two or more
persons who are closely involved with each other, e.g. in a conversation or a
chase scene; (b) using cuts to create an effect o f moving rapidly towards a
subject |
||
|
fade-in (Aufblende) |
from a black screen or ground, the gradual
emergence o f an image, which slowly becomes brighter until it reaches full
strength |
||
|
fade-out (Abblende) |
the gradual disappearance of an image until the
screen or ground is completely black; a device used to end a scene |
||
|
dissolve, dissolving shot or cross-fade (Mischbild) |
following a fade-out with a fade-in in order to
move slowly from one scene to the next |
||
|
Miscellaneous |
|||
|
backlighting |
filming a person or event against a background of
light, especially the sun, which produces an idealized, sometimes romantic
effect |
||
|
background music |
the music accompanying scenes "What
~ would you use?" "What
effect does the ~ have?" |
||
|
camera operator |
the person behind the camera(s); in major
productions, the head of the camera team is usually called the director of
photography |
||
|
caption |
words that are shown on a cinema or television
screen, e.g. to establish the scene of a story |
||
|
clip |
short piece of film or video. |
||
|
composition |
the arrangement of people or things in a
painting, photograph, film scene, etc. |
||
|
(film) director (Regisseur) |
the person responsible for the artistic
production of a film, i.e. the lightning, camera work, action, and the
actors' interpretation of their roles "What
do you think the director's intention is?" "Why
does the director use this shot?" |
||
|
credits (Vor-/ Abspann) |
list of people who helped to make a film or
programme. |
||
|
editor |
the person responsible for arranging the camera
shots and splicing (cutting / pasting) the shots together |
||
|
film transcript |
transcript of the final film according to the
individual shots giving field size, camera angle, camera movement, action,
dialogue etc. |
||
|
footage (das Material) |
Piece of film or video. "Where
is the ~ being filmed from?" "What
sort of TV programme uses footage like this?" |
||
|
freeze-frame (eingefrorenes Bild) |
effect when all movement is stopped. |
||
|
motion picture |
a US and Canadian term for film |
||
|
producer |
the person responsible for the overall
organization, especially the financing and marketing, of a film or TV
production |
||
|
scene |
a shot or a series of shots that deal(s)
with a single action |
||
|
screenplay (Drehbuch) |
film script with dialogue, location descriptions
and some camera angles and movements. |
||
|
sequence (Teil des Filmes) |
Connected piece of film, perhaps a complete scene. "What
does the ~ of close-up and extreme cluse-up shots focus on?" |
||
|
setting |
the location of a film "If
you were the director of the film, what kind of setting would you choose?" |
||
|
shot (Einstellung) |
Single piece of camera work, e.g. a cutaway. "What
sort of shot has to be used for an event like this?" "Watch
the film as far as the first shot of Ben in his room." "The
director uses ...shots to ..." |
||
|
soundtrack |
All sound for a film, including voices and music. |
||
|
still (Standbild, auch: das Insert) |
Single frame of a film, like a photo. "What
could the connection between the title and the stills?" |
||
|
storyboard (Aufnahmeplan) |
series of simple pictures showing the sequence of
main shots, often with notes an camera angles and movements. |
||
|
subtitle (Untertitel) |
Printed words, usually below the picture, and
usually used to translate dialogue in a foreign film. |
||
|
time-lapse photography (Zeitraffer, auch: Einzelbildschaltung) |
Technique of filming very short bursts from a
fixed position at fixed time intervals, so that action appears very rapid when the film
is played back at normal speed. |
||
|
(voice)off |
not to be seen but to be heard (especially a
narrator, a character voicing thoughts or a news correspondent commenting on
pictures that are being shown) |
||
|
voice-over (Filmkommentar) |
commentary heard by the viewer without the
speaker being in-shot. Often used in documentaries. "The
voice-over comments break the scene into four sections." |
||